Molecules in Motion
How Interactive Tech is Revolutionizing Pharmacy Education
Article Navigation
The Molecular Mastery Challenge
Pharmaceutical students face a unique cognitive hurdle: they must visualize intricate molecular interactions that dictate drug behavior—processes occurring at scales of one-billionth of a meter. Traditional teaching tools struggle to convey this invisible world, leaving students reliant on abstract formulas and 2D diagrams.
As medicinal chemistry grows increasingly complex, educators face a critical question: How do we make the unseen tangible? Enter PhET Interactive Simulations—a game-changing bridge between quantum-scale phenomena and future pharmacists' understanding 2 6 .

The Digital Alchemy Transforming Pharmacy Education
Why Pharma Students Struggle
Pharmaceutical chemistry demands mastery of three interdependent dimensions:
- Macroscopic (observable drug properties)
- Molecular (atomic arrangements and bonding)
- Symbolic (chemical equations and formulas)
Without tools to connect these perspectives, students memorize rather than comprehend. A 2022 Malawi study found students taught traditionally scored only 42.7% on conceptual tests—below the 50% mastery threshold 5 .
PhET's Cognitive Toolkit
Developed by Nobel laureate Carl Wieman's team, PhET simulations leverage:
- Implicit Scaffolding: Interfaces guide discovery without rigid instructions 2
- Dynamic Feedback: Real-time visualization of molecular collisions/reactions
- Multimodal Learning: Sliders, drag-and-drop atoms, and animated outputs
"Simulations create 'aha moments' when abstract symbols transform into interactive systems." — PhET Design Team 2
For pharmacy curricula, this means students can:
Case Study: Proof in Pharmaceutical Practice
The Oscillation & Waves Experiment (Malawi 2022)
Objective
Test if PhET improves understanding of wave properties critical for drug delivery systems (e.g., ultrasound-mediated release).
Methodology
- Participants: 280 pharmaceutical students (mean age 17.5) split into control/treatment groups
- Pre-Test: Both groups assessed on wave fundamentals
- Intervention:
- Control: Textbook diagrams + lectures
- Treatment: 3-week PhET module (e.g., "Wave on a String" sim)
- Post-Test: Identical conceptual questions + motivation survey
Results
Table 1: Academic Performance Gains
| Group | Pre-Test Avg (%) | Post-Test Avg (%) | Gain (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 42.7 | 58.1 | 15.4 |
| PhET | 44.2 | 78.9 | 34.7 |
Statistical analysis confirmed the 20.8% difference resulted from PhET (p < 0.01), not student variables 5 .
Table 2: Motivation Shifts (Post-Intervention)
| Motivation Factor | PhET Group Increase | Control Change |
|---|---|---|
| Self-Efficacy | +38% | +6% |
| Active Learning Strategies | +41% | -2% |
| Attitudes Toward Tech | +52% | +11% |
"Seeing sound waves manipulate particles felt like operating a nano-delivery drone. I finally grasped targeted drug design." — Study Participant 5
Performance Comparison
The Pharmaceutical Scientist's Digital Toolkit
Essential PhET Sims for Pharmacy Education
| Simulation | Key Features | Pharma Application |
|---|---|---|
| Build a Molecule | Drag-and-drop atoms; 3D rotation | Visualize drug stereochemistry |
| Reactants, Products & Leftovers | Varying reaction conditions | Predict drug synthesis yields |
| Acid-Base Solutions | pH meter; molecule concentration sliders | Study ionization of aspirin |
| Molarity | Solute/solvent manipulator | Design injectable concentrations |
| Membrane Channels | Ion diffusion controls | Model drug transport across barriers |
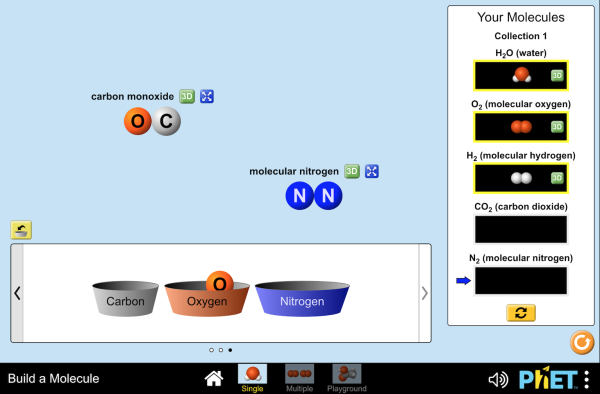
Build a Molecule
Interactive molecular construction with real-time 3D visualization.
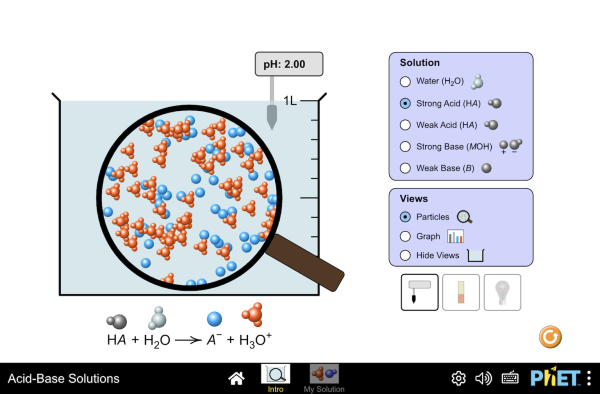
Acid-Base Solutions
Explore pH effects on molecular structure and behavior.

Membrane Channels
Simulate drug transport across biological barriers.
Beyond the Classroom: Future Frontiers
PhET's Expanding Impact
- Personalized Pacing: Students replay complex reactions until mastered—impossible with lab equipment 6
- Error as Exploration: "Breaking" simulations teaches system limits safely (e.g., oversaturating solutions)
- AR Integration: Upcoming mobile apps will project molecular interactions onto physical lab spaces
The Prescription for Tomorrow's Pharmacists
PhET simulations don't replace labs; they deepen them. When Malawi pharmaceutical students used both physical experiments and simulations, conceptual retention increased 2.3× compared to either approach alone. As computational drug design accelerates, these digital tools transform passive learners into active molecular architects—proving that sometimes, the most powerful educational tools are ones we can't physically touch 2 5 6 .
Try It Yourself
Experience the molecule builder at phet.colorado.edu – no login required.